Integrated Control Strategies for Freeway Bottlenecks with Vehicle Platooning
Keywords:
Freeway bottleneck, variable speed limit, vehicle platooning, deep reinforcement learningAbstract
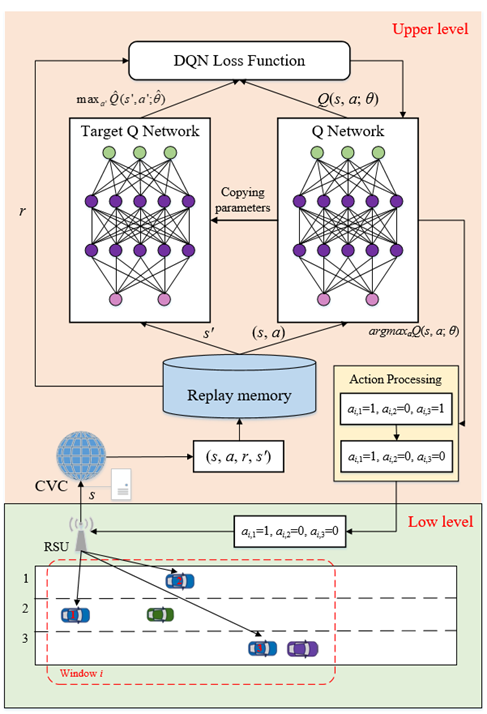
Freeway bottlenecks caused by traffic incidents contribute significantly to large-scale traffic congestion. Traditional strategies, including variable speed limit (VSL) and ramp metering, are commonly used for freeway traffic congestion management. Recently, vehicle platooning has become a promising way to alleviate traffic bottlenecks. This work proposes a novel framework that combines VSL and vehicle platooning for freeway bottleneck, referred to as VSL-VP, in mixed traffic of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) and human-driven vehicles (HDVs). First, the upstream road of a bottleneck is divided into two segments, called the former and the latter ones. VSL limits vehicle speed at the former segment, thereby reducing inflow traffic to the latter one. Then, deep reinforcement learning is employed for CAV platooning at the latter segment, where low traffic flow density and large car-following distance create conditions for smooth lane change and platoon formulation of CAVs. Simulation results demonstrate that VSL-VP significantly enhances the bottleneck throughput and reduces traffic congestion at elevated levels of CAV penetration rates.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Green Manufacturing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


