Human-Robot Collaborative Disassembly Profit Maximization via Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer
Keywords:
Human-robot collaboration, circular disassembly line, mixed-integer programmingAbstract
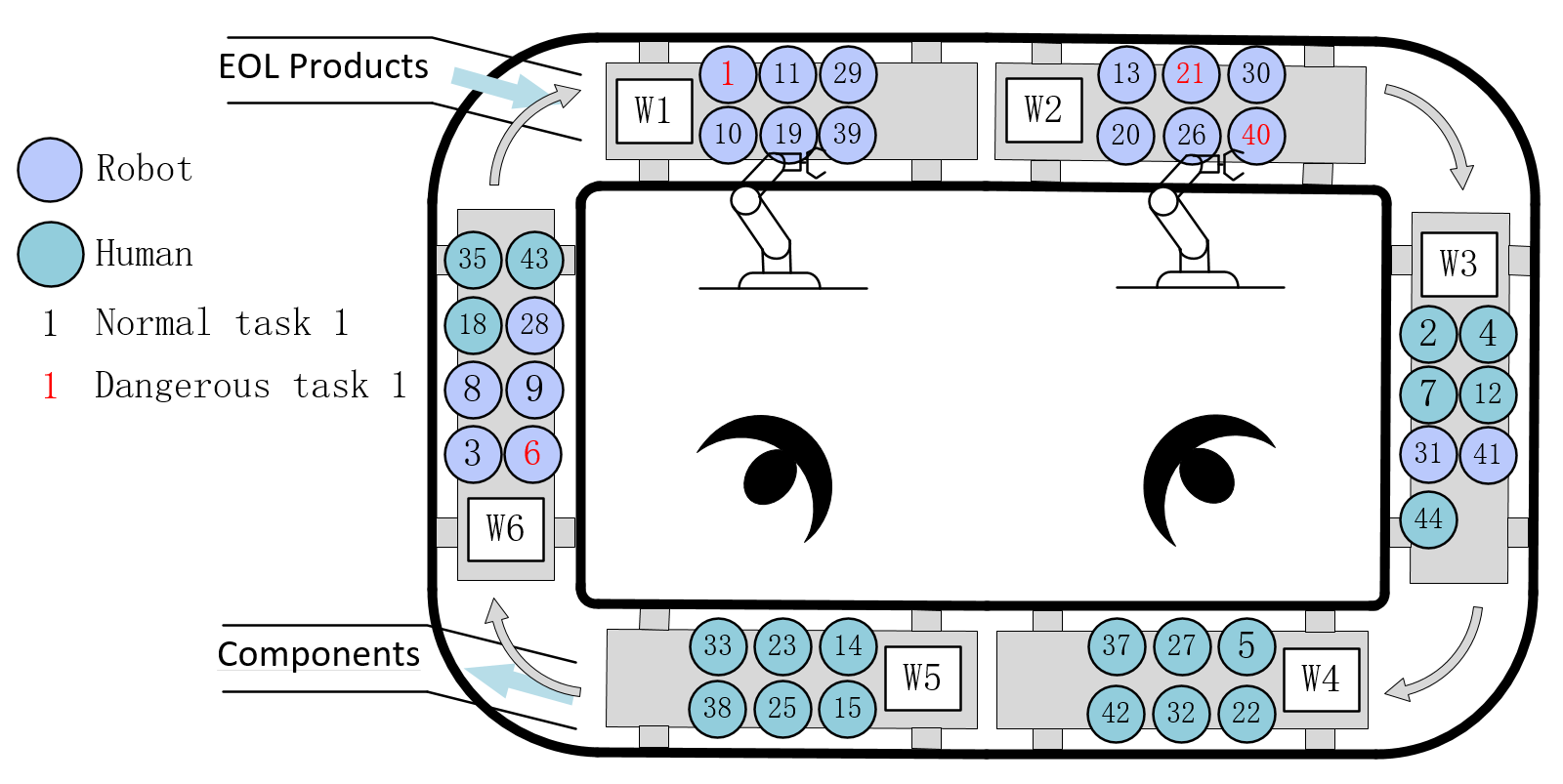
With the continuous advancement of modern technologies, a growing number of new products feature increasingly complex designs. The complexity of these products poses significant challenges to the planning and execution of their disassembly processes. This work proposes a human-robot collaborative disassembly solution to address such challenges. A circular disassembly line layout enables the cyclic assignment of tasks between human operators and robots. This layout overcomes the time and spatial limitations inherent in traditional disassembly lines. A human-robot collaborative circular disassembly line balancing problem is formulated, along with its integer mathematical programming model aimed at maximizing disassembly profit. The competency of the model is verified by applying the commercially available software CPLEX to small-scale product examples. An improved grey wolf optimizer is proposed to solve large instances that CPLEX fails to address. Its experimental results are compared with those of several representative intelligent optimizers. The results indicate that it surpasses existing methods, highlighting its potential as a promising solution for industrial applications.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Green Manufacturing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


