Intelligent and Adaptive Task Migration in Vehicular Edge-Cloud Computing Environments
Abstract
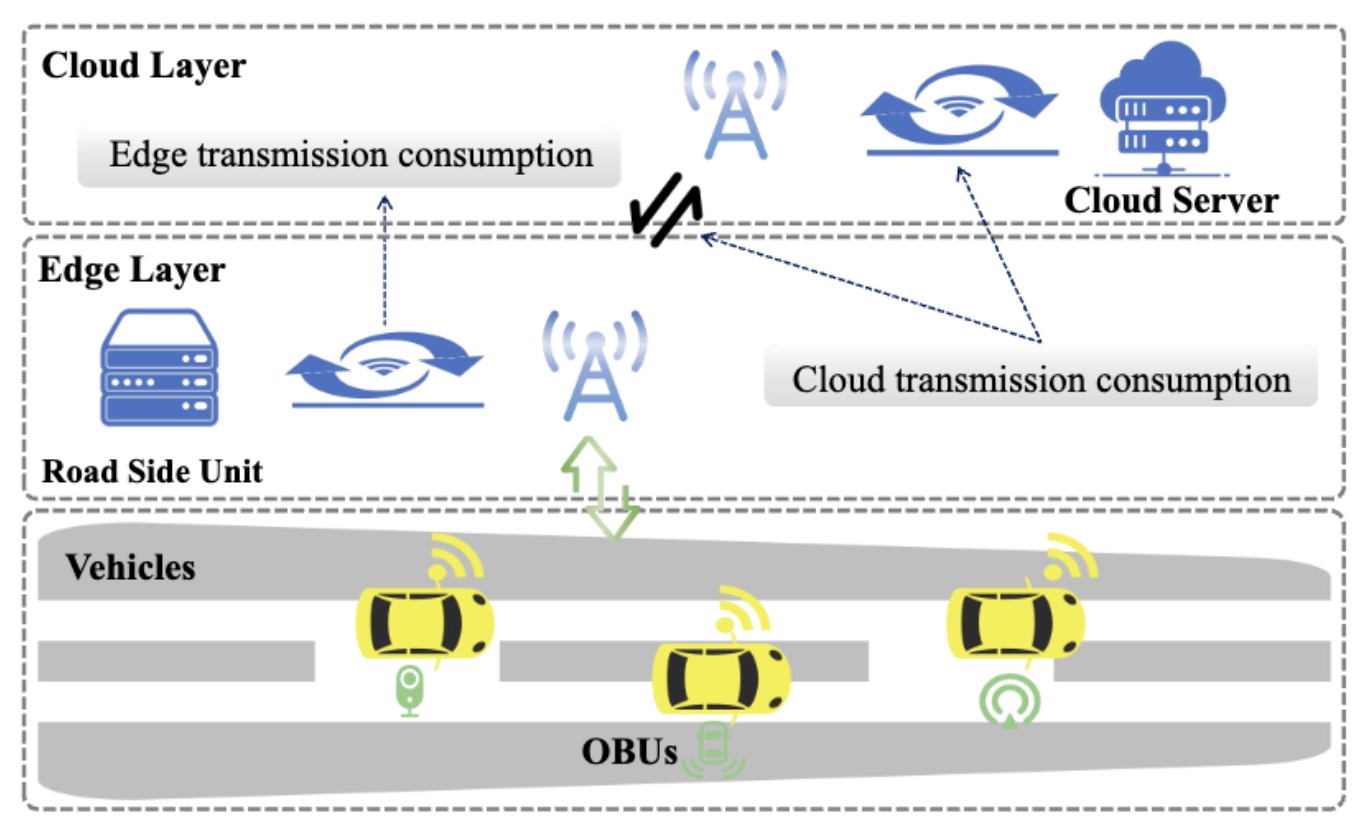
The growing prevalence of computationally intensive applications such as autonomous driving and in-vehicle infotainment places a substantial energy burden on modern vehicles. To mitigate this challenge, computational offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) has attracted increasing attention. However, existing offloading solutions for VEC often face limitations in practicality, slow convergence, or unsatisfactory optimization quality. To overcome these challenges, this work designs Variational Autoencoder Enhanced Lévy Differential Evolution Offloader (VELO), an optimization framework for task offloading in VEC environments. VELO dynamically selects between roadside units (RSUs) and cloud servers as offloading targets, aiming to reduce system energy consumption. The framework incorporates a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) for dimensionality reduction to accelerate inference and integrates a Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm augmented with a Lévy flight strategy to improve optimization quality. Experimental results show that VELO achieves competitive results, effectively lowering system-level energy consumption while preserving rapid convergence. VELO offers a promising solution to reduce the computational load on next-generation vehicle applications and supports the development of energy-efficient, low-carbon intelligent transportation systems.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2026 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Green Manufacturing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


