Curating Dataset Pipelines to Train Medical Chatbots on Early Sepsis Detection
Keywords:
Sepsis, Large language model, Medical Chatbot, Lexical Analysis, Semantical Analysis, LLL as a JudgeAbstract
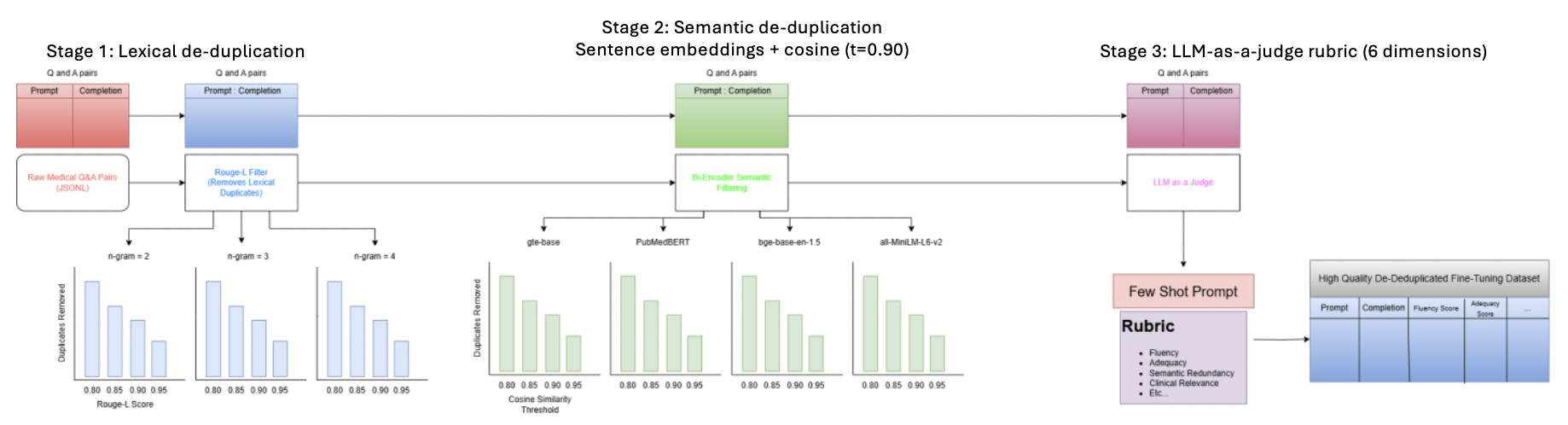
Sepsis is a critical medical condition that arises when the body’s response to infection causes life-threatening organ dysfunction. Despite increasing awareness and the use of protocol-driven management strategies, early diagnosis remains a persistent challenge in clinical practice, especially in high- pressure settings such as emergency departments and ICUs. Nurses, as first responders, are crucial in identifying early signs, but often work under cognitive overload and ambiguity of the protocol. Large language models (LLMs) represent frontier neural network techniques that use self-supervised learning algorithms to process and understand human languages or text. This work focuses on building a robust data gathering pipeline in order to ultimately create an interactive clinical chatbot fine- tuned on sepsis-specific knowledge. The pipeline consists of a three-step process, namely lexical analysis, semantic analysis, and Q&A quality evaluation, that utilizes artificial intelligence to collect training data in novel ways. It provides a feasible and cutting-edge framework for LLM-based chatbot design and development.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2026 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Green Manufacturing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


